A low-radiation, non-invasive diagnostic imaging test is used to evaluate the circulation to the heart muscle and detect various heart conditions, including heart muscle disorder. This condition occurs when the heart muscle becomes thickened, which can lead to an abnormal heart rhythm and اسکن هسته ای قلب potentially life-threatening complications.
High blood pressure, faulty heart valves, or coronary artery disease often cause cardiac hypertrophy. It can also be a result of an higher blood pressure placed on the heart muscle, which can occur in athletes or individuals with cardiac conditions.
During a heart imaging exam, a small amount of tracer compound is injected into the patient's bloodstream. This material is designed to attach to the heart muscle cells and emits low levels of radiation, which is then detected by a radiation detector. The camera produces images of the heart, highlighting areas of normal and abnormal blood flow.
In cases of cardiac hypertrophy, the heart imaging test can help diagnose the condition by detecting areas of the heart muscle that have reduced blood flow. The scan can also evaluate the heart's structure and function and provide information on the size and function of the heart chambers.
The diagnostic tool is a safe and effective diagnostic tool, but it does come with some risks. The small amount of radiation used in the test is not enough to cause any significant harm, but it can cause temporary side effects such as short-lived side effects.
Most patients can return to their normal activities immediately after the test, but in some cases, patients may be required to wait for a short period of time before leaving the testing area. Patients should inform their doctor about any medication they are taking, especially medications that may affect the test results.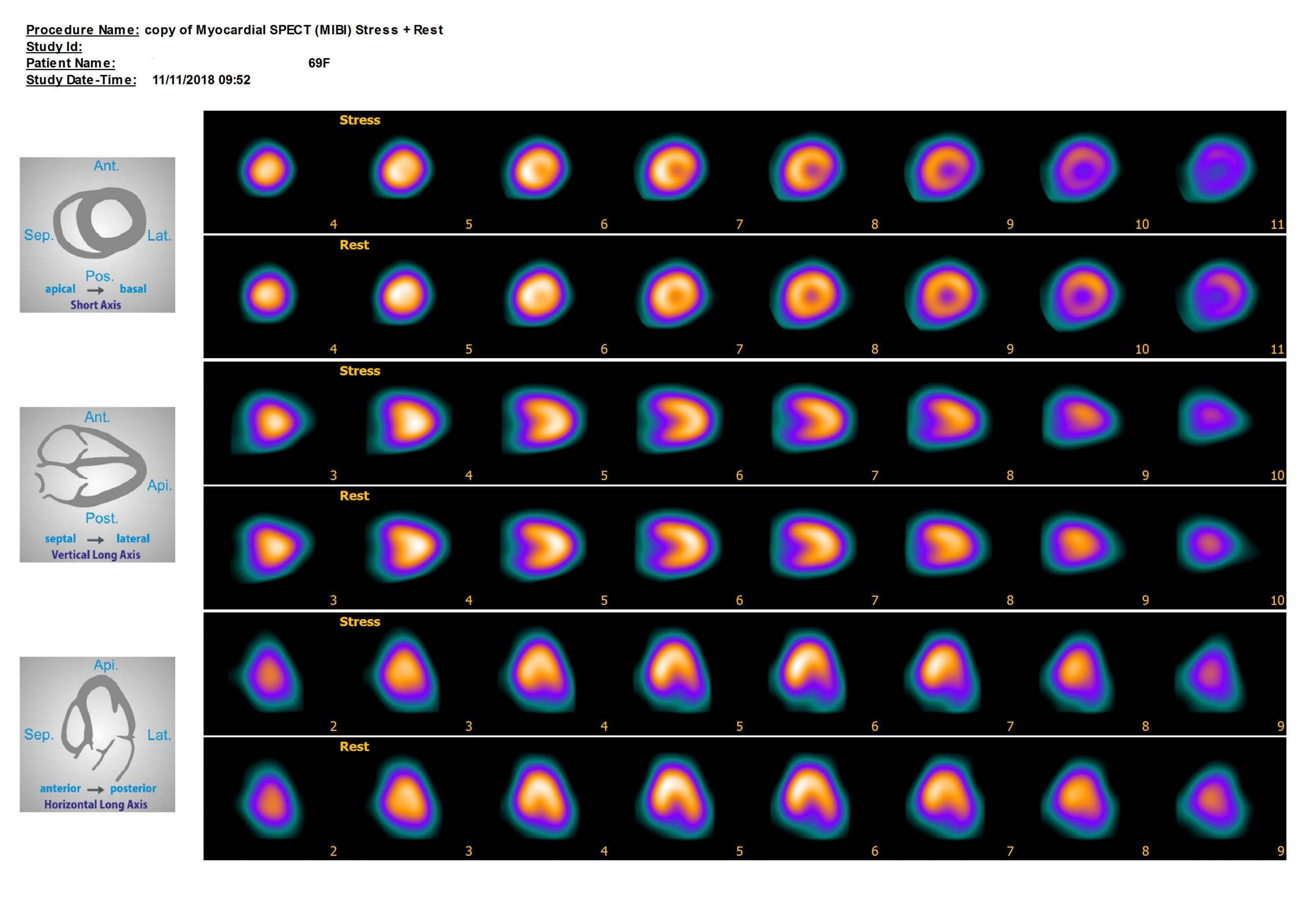
In conclusion, a nuclear heart scan is a valuable diagnostic tool used to diagnose cardiac hypertrophy and other heart conditions. The test is reliable and non-invasive, and it provides valuable information on the heart's electrical activity. While the test does come with some risks, the benefits of early diagnosis and treatment far outweigh the potential risks.
High blood pressure, faulty heart valves, or coronary artery disease often cause cardiac hypertrophy. It can also be a result of an higher blood pressure placed on the heart muscle, which can occur in athletes or individuals with cardiac conditions.
During a heart imaging exam, a small amount of tracer compound is injected into the patient's bloodstream. This material is designed to attach to the heart muscle cells and emits low levels of radiation, which is then detected by a radiation detector. The camera produces images of the heart, highlighting areas of normal and abnormal blood flow.
In cases of cardiac hypertrophy, the heart imaging test can help diagnose the condition by detecting areas of the heart muscle that have reduced blood flow. The scan can also evaluate the heart's structure and function and provide information on the size and function of the heart chambers.
The diagnostic tool is a safe and effective diagnostic tool, but it does come with some risks. The small amount of radiation used in the test is not enough to cause any significant harm, but it can cause temporary side effects such as short-lived side effects.
Most patients can return to their normal activities immediately after the test, but in some cases, patients may be required to wait for a short period of time before leaving the testing area. Patients should inform their doctor about any medication they are taking, especially medications that may affect the test results.

In conclusion, a nuclear heart scan is a valuable diagnostic tool used to diagnose cardiac hypertrophy and other heart conditions. The test is reliable and non-invasive, and it provides valuable information on the heart's electrical activity. While the test does come with some risks, the benefits of early diagnosis and treatment far outweigh the potential risks.


댓글 달기 WYSIWYG 사용